Network Note For Debug
This is my network note which record different linux and debug command
Debug Using tool
Nmap port scan
Scan port can use either:
nc -vz: quick, lightweight probe (good for QA spot checks).nmap: more detailed: can scan ranges, detect service versions, OS fingerprints, etc.
1 | nmap -Pn -p 21 172.21.201.16 |
Scan port option:
-Pn: don’t ping first (treat host as alive)-p 21: scan only port 21
Netcat: scan and send traffic
The nc command allow you to debug like send a small traffic or scan port just like nmap
Scan if a port is open like nmap
Syntax:
nc -vz ip-add port
-v: verbose-z: just scan for listening service (don’t send data)
- scan http
1 | nc -vz 172.21.201.250 8080 |
- scan ftp
1 | nc -vz 172.21.201.250 21 #ftp |
Output tells you if the port is open, closed, or filtered.
Send traffic
If DUT NOT support FTP related command, when you want to debug field side issue, to make sure traffic is working or not. You can only use http , or ftp related potocol to verify it. Since use remote like ssh to debug, so the only method is use the nc command to check traffic work or not under ssh.
If you want to verify traffic you have to first run nf command on local pc, and use tcpdump on field side ssh server to make sure you pass traffic really psss. I
Environment might look like this:
CPE(send traffic ex: nf) <——>(Lan) CPE (Wan)<——->Internet<——–>SSH field Router(tcpdump)
send http
Netcat will try to connect to host 172.21.201.250 on TCP port 8080
1 | nc 172.21.201.250 8080 |
If something is listening there (like a web server), the connection opens and anything you type will be sent to it.
If nothing is listening, you’ll get a timeout or connection refused, aslo mean netrwork unreachable
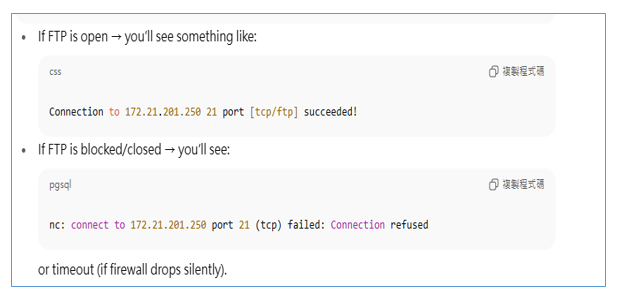
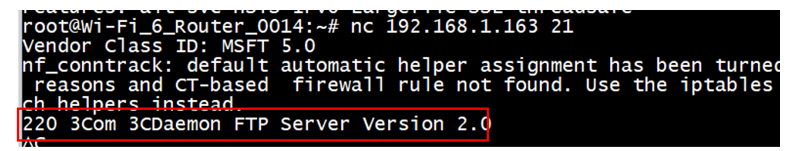
Send ftp
I can use this command below to make ftp connection
1 | nc Ftp-IPaddress 21 |
Run server as listen
- Host 1 as listen server
1 | nc -l -p 9090 |
Listens on TCP port 8080.
Any client that connects can send/receive text.
- Host 2 connect and send traffic
1 | nc <Host 1 IP> 9090 |
Quick file transer
1 | # on Receiver |
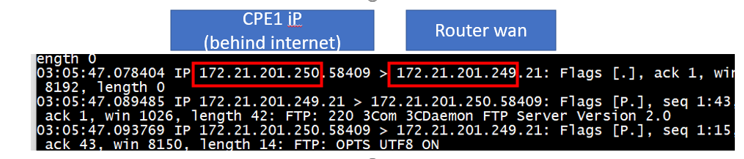
tcpdump capture packet
In the top we use the nc command to send traffic, you also need to see the packet flow to make sure it really pass.
TCP 3 hand shake:
syn->syn/ack->Ack
If the traffic really make connection success then your packet should see the three flow
Capture packet for 21 ftp
1 | tcpdump -i eth4_v0 -nn port 21 |
Save traffic as packet
1 | tcpdump -i eth1.1035 -s 0 -w /tmp/ap.pcap & |
Curl
Some DuT uses a light weight curl, which mean not support ftp or other feature. You can use curl --version to check.
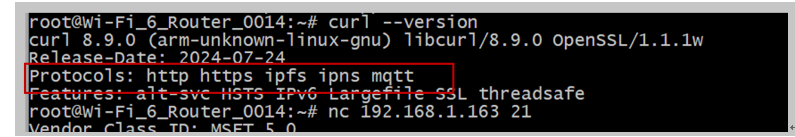
This mean even though you don;t have a ftp installed in your system, but you can use curl, however this version curl don’t even support ftp.
To use ftp right now is you need to use the nf command
Curl webpage
1 | curl http://localhost/test1234/test.html |
Fetch a file and store in a local file [-o option]
Syntax:
curl -o [name of output] [url name]
o: is rename another file
1 | curl -o test.html http://127.0.0.1/tt.html #download and rename to test.html |
Curl ftp connection
- username and password connection
1 | curl -u user:pass ftp://192.168.1.163/ |

- Download anonymous account
1 | curl -u anonymous:anonymous -O http://192.168.3.181/iperfcommand.txt |
- upload
1 | curl -u anonymous:anonymous -T [file name] [url] |
tftp
- linux or console
1 | #upload to lcoal side from console |
- window tftp might look different
Syntax:
tftp -i [IP ADD] [PUT|GET][ FILE NAME]
-g: get file-r: remote-p: put file-l: loca
1 | #download |
scp upload download file
scp
1 | #upload |
using sshpass without type password
sshpass bypass the interactive password prompt for scp (and ssh).
install: apt install sshpass
syntax::
sshpass -p 'server passw' scp <filename or path> <sshhostname>:<destinationPath>
- Example
1 | sshpass -p 'nr@Gnb' scp l1app-0809 nrgnb@192.188.4.21:/home/nrgnb/Downloads/ |
- script
1 | sshhostname="nrgnb@192.188.4.21" |
Ping command
Ping with timestamp
- Linux
1 | $ ping linuxbuzz.com | while read pong; do echo "$(date): $pong"; done |
Add into shell script
1 | #!/bin/bash |
Reference:
https://www.linuxbuzz.com/enable-timestamp-linux-ping-command
- PowerShell
1 | ping.exe -t <IP> | Foreach{"{0} - {1}" -f (Get-Date -f "yyyyMMdd HH:mm:ss"),$_} |
CPU Busy
You can either use:
- method1
1 | for i in 1 2 3 4; do while : ; do : ; done & done |
- method2
1 | sha1sum /dev/zero & |
kill process: kill sha1sum
- Script:
1 | #!/bin/bash |
Change permission: chmod +x cpu_load.sh
Run Script: ./cpu_load.sh &
Reference:
https://dev.to/abstractmusa/how-to-simulate-high-cpu-usage-on-aws-ubuntu-instances-for-testing-and-performance-optimization-1f5f >> https://superuser.com/questions/443406/how-can-i-produce-high-cpu-load-on-a-linux-server